top of page

Turbomachinery > Cavitation
Impact of Inlet Flow Conditions on Turbopump Stability

KSLV-1 (www.kslv.or.kr)
Liquid propellant rockets are the most advanced launchers which facilitate thrust control. Turbopumps, which pump liquid fuel and oxidizer into the combustion chamber, are some of the most difficult components to design and manufacture. In turbopumps, an inducer is placed in front of the impeller to enhance performance. (cavitation prevention, increasing suction performance, etc.) Like the turbopump, the inducer suffers from cavitation and consequently degrades suction performance. Cavitation also gives rise to instabilities such as rotating cavitation and cavitation surge.

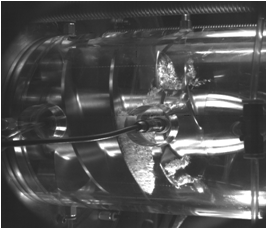
KSLV 70- ton turbo pump(left) and Cavitating inducer(right)
Many studies have been done on the inducer performance, cavitation instabilities, and thermodynamic effects. However, the effects of inlet flow distortion on the inducer performance have not yet been investigated.

Schematic of rocket fuel system (Merlin 1C engine, spaceX, www.spacex.com)
This research aims to investigate the inlet flow non-uniformity effects on the inducer performance. The research questions are as follows 1) What is the physical mechanism of inducer cavitation? 2) How do cavitation characteristics and suction performance change when flow is distorted? Static pressure and unsteady pressure measurements, inducer flow field measurements, and flow visualization inside the inducer will be implemented. The results of this investigation will directly aid development of the KSLV to be launched in 2018.

bottom of page
